World Sickle Cell Day: Know Your Status!
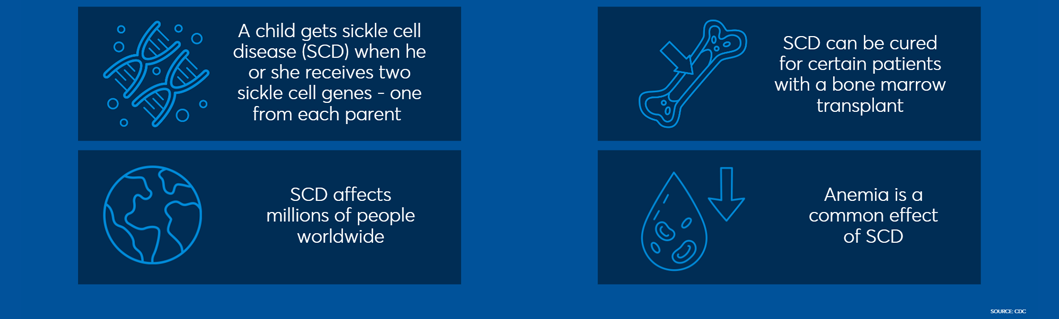
World Sickle Cell Day is a time to raise awareness and understanding about sickle cell disease (SCD), a genetic blood disorder that affects 90,000 to 100,000 Americans ¹. It is common for individuals to become aware of their SCD status only when they have children.
However, thanks to advanced technology, there are now easily accessible tests that can provide valuable information about SCD status in both children and adults. In this article, we will learn more about SCD, including the different testing options that can inform you of your SCD status.
Basics of Sickle Cell Disease
Sickle cell disease (SCD) causes sickle shaped- or crescent-shaped red blood cells. These abnormally shaped blood cells can stick together, blocking blood flow and oxygen from reaching all parts of the body.
 Symptoms of SCD vary from person to person, but might include ²,³:
Symptoms of SCD vary from person to person, but might include ²,³:
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath
- Delayed growth
- High blood pressure
- Chronic pain
- Blood clots
- Stroke
- Heart failure
SCD can result in many different complications, including kidney and liver damage, organ damage, anemia, and frequent infections ³.
Causes of Sickle Cell
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is caused by certain changes in the DNA of a gene called HBB, which are referred to as pathogenic variants. Each person inherits two copies of the HBB gene, one from their mother and the other from their father. SCD occurs when both copies of the HBB gene have these DNA changes.
If someone has a DNA change in only one copy of the HBB gene, they do not have SCD. Instead, they have sickle cell trait. This means they are carriers for SCD and can pass the DNA change on to their children, but typically do not show signs of SCD themselves.
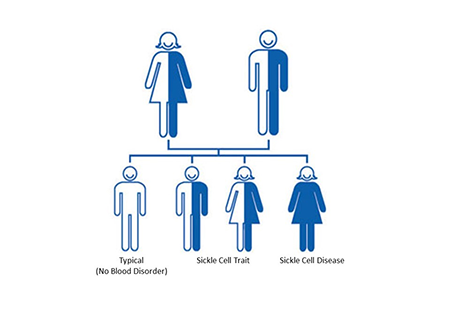
 If both parents are carriers for SCD, each of their children will have a 1 in 4 chance of having SCD, and a 1 in 2 chance of being carriers themselves ⁴.
If both parents are carriers for SCD, each of their children will have a 1 in 4 chance of having SCD, and a 1 in 2 chance of being carriers themselves ⁴.
Testing for Sickle Cell
Genetic testing is a trustworthy way to find out if someone has SCD or sickle cell trait. When a doctor suspects SCD or a similar blood disorder, they may request genetic testing along with other blood tests. This type of testing focuses on the HBB gene and can identify the specific DNA changes responsible for causing SCD.
If a person is diagnosed with SCD, sickle cell trait, or another inherited blood disorder, it is usual to screen their partner to assess the likelihood of their children inheriting SCD. If a person receives a positive genetic testing result for the HBB gene, it is important for them to consult with a genetic counselor. A genetic counselor is a healthcare professional who specializes in genetics and can provide guidance and support.
SCD is regularly checked for through newborn screening. Newborn screening is a special test conducted when a baby is 1-2 days old, which looks for serious but rare health conditions that can be treated. Each state has its own set of guidelines, but SCD has been included in the newborn screening panel of every state since 2005 ⁵. If a baby tests positive for SCD during the newborn screen, further diagnostic testing is often conducted to confirm whether they have SCD or sickle cell trait.
Risk Factors of Sickle Cell
Sickle cell disease affects millions of people worldwide. It is most common among people whose ancestors come from certain regions, such as ²:
- Africa
- Mediterranean countries such as Greece, Turkey, and Italy
- The Arabian Peninsula
- India
- Spanish-speaking regions in South America, Central America, and parts of the Caribbean
Sickle cell disease is the most common inherited blood disorder in the United States, and it disproportionately affects those with African or Hispanic ancestry ⁶. Sickle cell trait affects approximately 1 in 10 African Americans ⁷.
For More Information
Although complications from SCD and other blood disorders can be serious, treatment and monitoring can help prevent complications and improve quality of life. Individuals who believe that they may have SCD or another blood disorder should speak with their doctor.
HNL Genomics offers carrier screening and other genetic tests that can assess the risk of genetic disorders like SCD. If you are determined to be a carrier for SCD, HNL Genomics will offer free testing for SCD to your reproductive partner. Talk to your healthcare provider to see if genetic tests, like carrier screening, are right for you.
For more information on SCD, you can visit The Sickle Cell Disease Association of America, American Sickle Cell Anemia Association, or the CDC’s website.
REFERENCES
¹ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2022, December 20). Sickle cell disease. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. https://www.cdc.gov/dotw/sickle-cell-disease/index.html.
² National Library of Medicine. (2020, July 01). Sickle cell disease. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. https://medlineplus.gov/genetics/condition/sickle-cell-disease/.
³ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2022, May 10). Complications of sickle cell disease. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/sicklecell/complications.html.
⁴ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2020, December 14). What is sickle cell trait? U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/sicklecell/traits.html.
⁵ Pagon, R. A., & Adam, M. P. (2022). Sickle cell disease. In Genereviews. National Library of Medicine. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1377/.
⁶ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2022, May 02). Data & statistics on sickle cell disease. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/sicklecell/data.html.
⁷ American Society of Hematology. (2023). Sickle cell trait. https://www.hematology.org/education/patients/anemia/sickle-cell-trait.